Classification of computers can be done based on purpose data handling and Functionality. In this guide, you are going to learn different types of computer and their significant differences along with their advantages and disadvantages.
According to the recent data by Statista, 90% of homes in the United States have computers. And in India, the percentage is up to 74.27%, and that’s huge.
As we discussed earlier, computers are classified according to data handling, Purpose and Functionality. And now we are going to discuss each type in the classification of computers one by one.
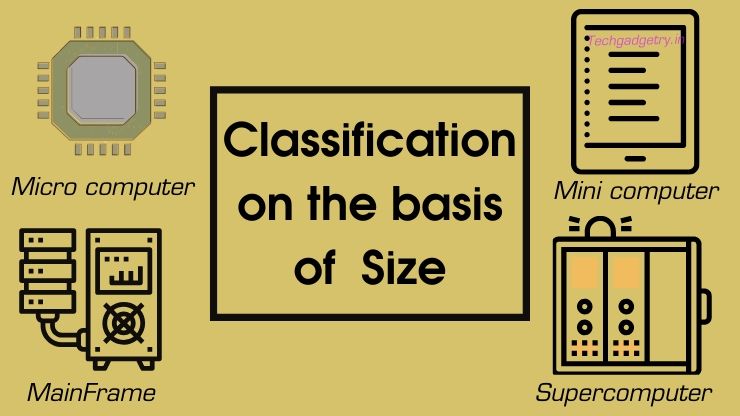
Classification of computers based on Size
There are four types of computers classified according to Size: Micro, mini, mainframe and supercomputer.
Microcomputers
Believe it or not, you are using this type of computer right now. Whether you have your smartphone in your hand, desktop, PC, laptop, PDA, tablet, gaming console or any navigation system, all are a part of microcomputers.
Advantages
- Fast Speed
- Cheaper
- Smaller in Size
- Easy to access
Disadvantages
- Internet Addiction
- Cyber gambling
- Game Addiction
How to stop offline speech recognition
Mini Computers
They are also k mid-range servers because they are more powerful than microcomputer in terms of power and capabilities. Minicomputers are multi-user systems, and many users are working simultaneously on the systems. For example, PDP-11, VAX, 7500 MAGNUM.
Advantages
- Greater Storage capacity
- Capable of handling more input/output devices
- Lightweight
- Can work with all operating systems
- Reduced power consumption
Disadvantages
- Fewer features than a standard desktop PC
- Dedicated Graphics card is missing
- Mini PCs have no Optical Drive
Mainframe
They support more than 100 users at a particular instant of time(Multi-user) and designed to handle vast volumes of data and information. Moreover, they can work with more than one processor instantaneously that’s why also referred to as multi-user or multiprocessor system.
Advantages
- Process data and run applications at high speed
- Reliable
- Secure
- Long-Lasting Performance
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Occupy more space
- Specialized skills are required to operate
Super Computers
This type of computer is the most powerful, fastest and most expensive model than can perform multiple tasks within a matter of seconds. It is known as super because it can solve difficult and complex problems very quickly.
Advantages
- Solve Bigger Problems
- Allows for Virtual testing
- Improving safety
- Lowering Costs
- Fastest
Disadvantages
- Overheating
- Expensive
- Storage and Bandwidth
- Processing Time
- Maintenance and support
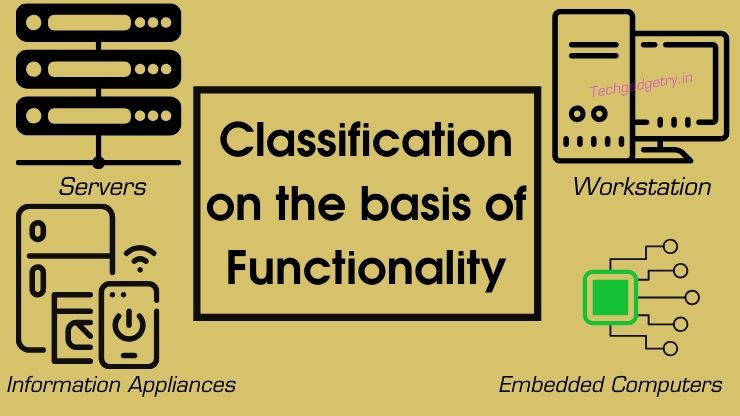
Types of Computer based on Functionality
According to Functionality, four different types of computers are classified as servers, workstation, information appliances and embedded processors.
Servers
This type of computer is dedicated to providing some specific services to you like security, database managing, many interconnecting connections etc. So, they are named according to function they perform like security server, database server, web server etc.
Probably you have seen this type of computer system in your school computer lab or the office room.
Advantages
- Allows centralized and automated backup systems
- Users can get access to shared data
- Adds Seamless connectivity
Disadvantages
- Expensive to purchase
- Specialist staff is required as a network manager
- If any part of the network fails a lot of disruption can occur
Workstation
These form of systems are designed to be used as a single user at a time but later turned into multi-user operating systems. Generally, they are found in day to day personal/commercial work as they are specially designed for the companies and firms.
Advantages
- Compatible with CPUs
- Bear high-quality graphics
- Applicable in research, engineering or other specialized fields
Disadvantages
- Repairing is difficult
- Bulky and Expensive
- Not Easily Available
Information Appliances
The portable devices that are designed to perform a limited set of tasks such as browsing the internet, playing multimedia, necessary calculations, etc. and are known as mobile devices.
Advantages
- Portable
- Infrared Beaming
- Variety of devices
Disadvantages
- Slower than PC
- Limited Memory
- Built-in obsolescence means OSs can’t get upgraded
Embedded Type Computers
These type of computers are designed to fulfil a limited set of requirements and doesn’t execute reboot or reset as it followed the operations from the non-volatile memory.
Advantages
- Reliable
- Easy for mass production
- Improved Product Quality
Disadvantages
- Hard to Maintain
- No room for technological improvements
- Complicated to backup the embedded files
Classification of Computers based on Purpose
Based on Purpose, they can be classified as either general Purpose or specific Purpose.

General Purpose Computers
This type of computers are capable of doing a large number of tasks such as scientific calculations, controlling security, word processing, managing database, etc. However, this happens at the expense of speed and efficiency that leads to slow down of the process.
Advantages
- Perform a wide variety of functions and operations
- Stores and execute different programs in its internal storage
Disadvantages
- Reduced Speed
- Less Efficiency
Specific-Purpose Computers
Those types of computers is designed to perform a narrow range functions with sharp focus and targeted speed. That’s why they also referred to as dedicated computers because a single task is devoted to each system to gain the maximum output for a particular job.
For example, traffic lights control system, robot helicopter, digital watch, weather forecasting etc. are the places where specialized computers are required to perform only one task. On the other hand, they lack versatility.
Advantages
- Fast Processing
- More Efficiency
Disadvantages
- Lack of Versatility
- Can’t used for other operations
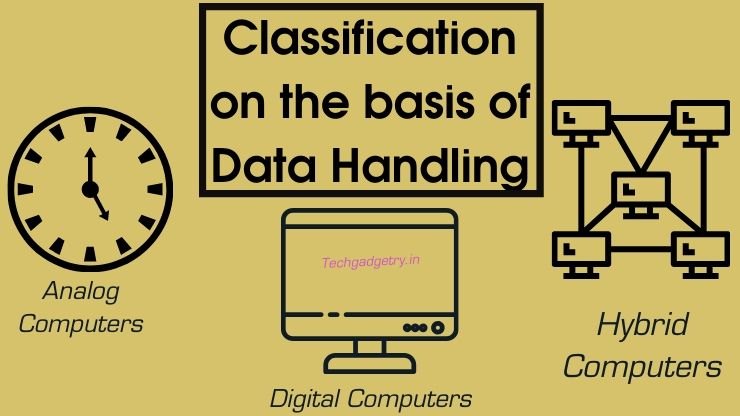
Types of Computer according to Data Handling/ Operating Principles
Classification of computers can also be done based on operations they performed and the methods they use to store and process the data information. They are of 3 types: Analog, digital and hybrid.
Analog Computers
This types of computer provides data in the form of continuous electrical signals with a specific magnitude, and they are used to handle a similar kind of data. They are very fast in their operations.
For example, the thermometer measures the length of a mercury column continuously. A traditional clock is covering the distance in the dial instantaneously, weight machine, speedometer, etc. are all measuring weight and speed every time.
Advantages
- Fast
- Portable
- Cheap
- Highly Sensitive
Disadvantages
- Wide range of complexity
- Lacks Memory
- Not Accurate
Digital Computers(DIPS)
These are the systems that allow data to store, create and recall whenever demanded during an indefinite period. According to classification of computers, they were also known as the digital information processing system as they take two separate values and add them together to get a meaningful result.
Each kind of data is electronically stored in the form of binary code, 0s and 1s, but the output is produced in understandable user format—for example, Business management.
Advantages
- More Accuracy
- Less Power requirement
- High Resolution
Disadvantages
- Less Sensitivity
- Expensive
- Not portable
Hybrid Computers
Those type of computers has the features of analogue as well as digital networks. Out of which, analogue part solves the problematic calculations, and the digital component serves as a controller, solving logical operations.
For example, they are used in industrial processes for the development of successful systems and various scientific applications. Another example is the Petrol pump where a processor converts the amount of petrol into quantity and price, in hospitals to measure the heartbeat of the patient.
Advantages
- Have features of both digital and analogue computers
- Fast Speed
- High Accuracy
- Online Data processing
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Requires more cable
- Complex design
- Difficulty in configuration
Bottom Line about Types of Computers
In a nutshell, there is various types of computer in the world, and we can classify them according to their Size, Functionality, purpose and data handling.
Feel free to ask any query in the comment section below.
Sharing is Caring!